The 3 types of bioplastics you need to know about
Bioplastics are materials with a growing weight within the polymer industry. However, there is a great deal of misinformation in this sector.
Do you know the different types of bioplastics? Do you know the main advantages of this type of material? If your answer is not clear, read on!
Plastics are an essential part of our lives. This type of material plays an essential role in the sourcing, shipping and storage of different products in our daily lives.
Today, there are alternative types of bioplastics for almost any type of plastic material and its corresponding application.
When we talk about “bioplastics” we are not talking about a single material, but rather about different types of materials that constitute a complete family with different properties and applications.
According to European Bioplastics, a plastic material is defined as a bioplastic when it is bio-based, biodegradable or both.
Benefits of bioplastics
Bioplastics bring multiple advantages. Among them, leading to more sustainable production and consumption and the search for new and more innovative materials.
The use of renewable sources to produce different types of bioplastics are key to increase resource efficiency in the sense of:
- That biomass can be used first for materials and the for generating energy
- Reducing carbon footprint and greenhouse gas emisissions
- Saving fossil resources by replacing them step by step
- Interested in the advantages of bioplastics in the food sector? We recommend this article: All you need to know about biodegradable food packaging
The 3 main types of bioplastics
Among the different types of bioplastics, biodegradable plastics are classified into different categories according to their origin and their compostability properties.
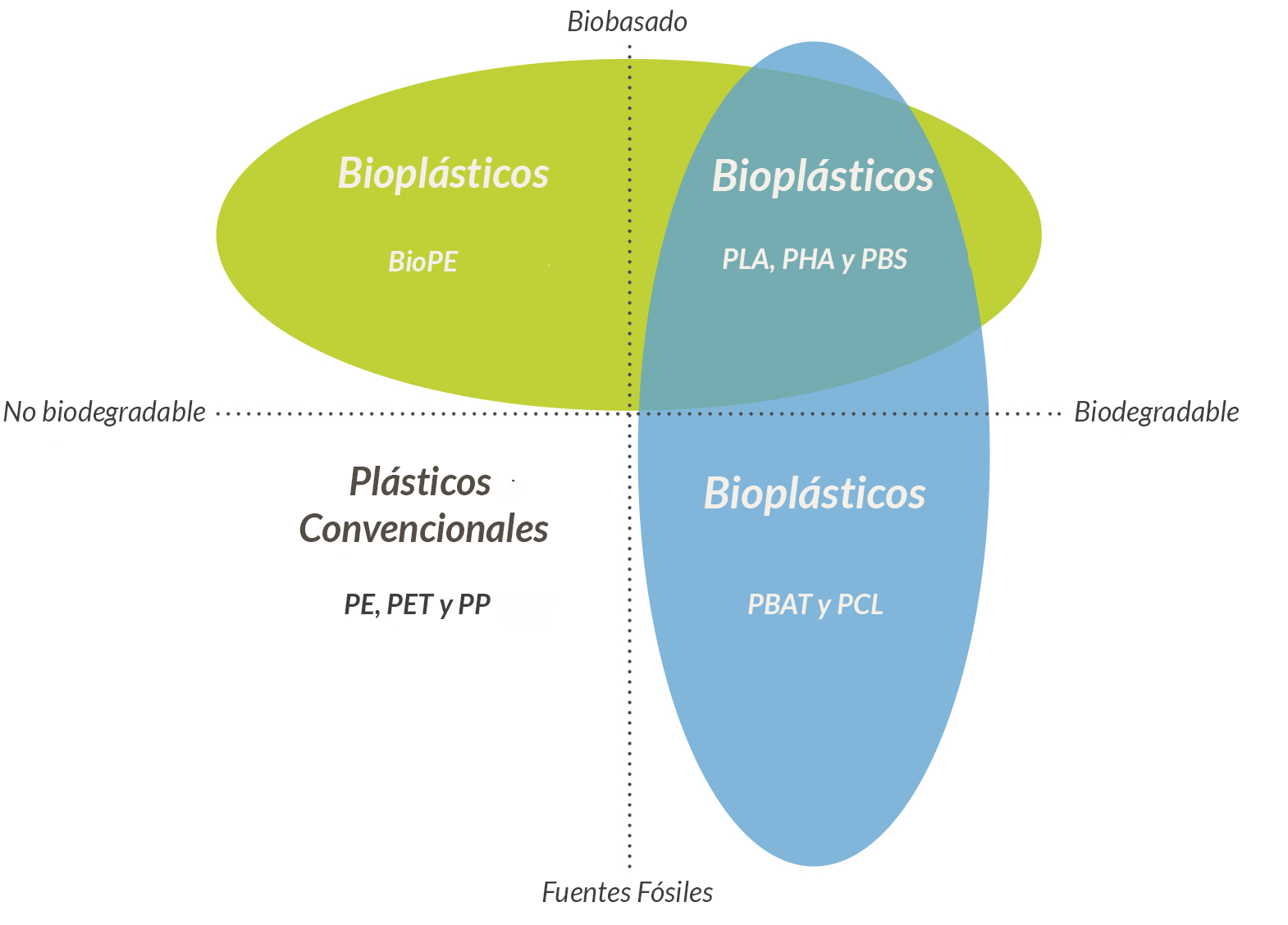
Bio-based plastics
When we talk about bio-based plastic, we mean that the carbon atoms of its molecule chains are taken from nature. In other words, it is “bio-based” in origin.
These types of bioplastics and their materials can be a good alternative to conventional plastics because they help us reduce the dependence that currently exists with respect to other sources of non-renewable origin such as petroleum.
As an example of a bio-based bioplastic, we find biopolyethylene (BioPE). Polyethylene is a type of bioplastic obtained from petroleum, while biopolyethylene is obtained from sugar cane.
However, despite their different origins, the properties of the material with respect to their biodegradability are the same. In other words, neither polyethylene nor biopolyethylene is biodegradable. Neither of these materials will be converted into natural substances through a chemical process carried out by microorganisms found in the environment.
There are other examples of non-biodegradable bio-based plastics such as BioPET . However, it is the same as BioPE. Their behavior is identical to that of their petroleum-derived versions. Which means, they are technically the same as their fossil counterparts, but with the advantage of reducing the carbon footprint of a product.
Biodegradable plastics
Biodegradation is a chemical process during which microorganisms found in the environment convert materials into natural substances such as water, carbon dioxide and compost.
The biodegradation process depends on the environmental conditions in which the material is found, such as location and temperature.
BIO-BASED DOES NOT MEAN BIODEGRADABLE
As explained above, the biodegradation property does not depend on the source of origin of the material, but rather is directly related to its chemical structure.
In other words, a 100% bio-based plastic may not be biodegradable and a 100% fossil-based plastic might be biodegradable.
- Did you know that during 2020 the total volume of bio-based polymer production was 4.2 million tons? Find out more statistics on bio-based polymers.
Fossil-based and biodegradable compostable plastics
There are types of bioplastics that meet both properties: biobased and biodegradable.
This group includes blends of starch and other biodegradable polymers well known to the bioplastics industry such as PLA or PHA.
The availability of such polymers represents a major step towards the achievement of the circular economy. These are materials that reduce the carbon footprint and subsequently biodegrade under the right conditions without leaving any trace of microplastics.
Materials such as PLA mark a new path in the packaging industry because they are showing that they have the potential to produce innovative and competitive new materials such as ZIMIA grades and thus shape the plastics industry.
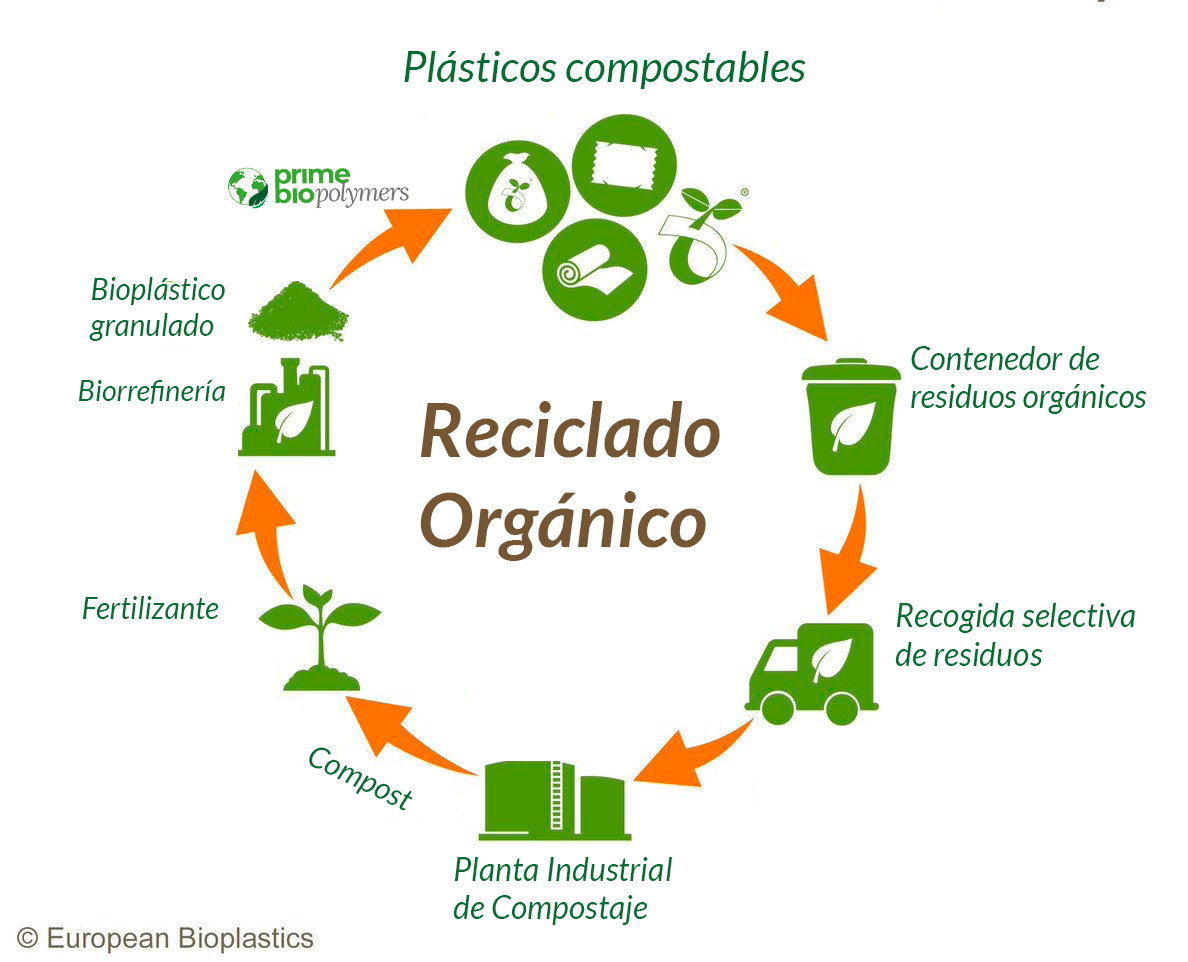
Why compostable?
The term “biodegradable” is rather ambiguous, as it does not specify the medium in which it degrades or the time it takes to do so. In other words, simply stating that a material is “biodegradable” without any standard specification is misleading. It should be accompanied by information such as the time frame, the level of biodegradation and the environmental conditions required.
For this reason, industry associations and organizations such as European Bioplastics recommend focusing on the condition of compostability, which is supported by the UNE-EN 13432.
In addition, there are certifications such as Ok Compost from TUV Austria that ensure that a material complies with the required compostability requirements.
In addition, these certifications have another great benefit: they differentiate compostables from products labeled as “oxo-biodegradable” or “oxo-degradable”, which do not meet the industrial compostability requirements of the UNE EN 13432 standard.
Prime Biopolymers for the development of different types of bioplastics
Taking into account the needs that must be covered to carry out the transition from conventional plastic to bioplastics, Prime Biopolymers develops tailor-made biopolymers. In this way, we achieve that the materials are fully adapted to the processes and machinery of our customers.
From Prime Biopolymers, as a result of our investment in innovation and development, we translate requirements such as transparency, fluidity and flexibility into a specific grade of compostable material that achieves a more environmentally friendly line of parts or packaging.
Bioplastic types: ZIMIA grades
Prime Biopolymers has standard grades of biobased and compostable bioplastics that are fully adaptable to different manufacturing methods. In particular, we have ZIMIA grades that are suitable for manufacturing by









