Everything you need to know about biobased plastics
There are many doubts that arise when talking about bioplastics: biobased plastics, biodegradable, compostable… Many concepts revolve around this industry that should be explained as clearly and concisely as possible.
According to European Bioplastics, a well known source in the sector, a biobased or partly biobased plastic es one that comes from renowable and natural raw materials, mainly of vegetable origin such as corn or sugar cane.
Biobasaded is not biodegradable
The adjective “biobased” only indicates that the carbon atoms of the molecule chains are taken from nature, i.e. they are of “bio” origin. A clear example of this is biopolyethylene (BioPE). This material can be obtained from sugar cane and has the characteristics of normal polyethylene, however, it is not biodegradable, so it will not be achieved from a chemical process in which microorganisms found in the environment convert the material into natural substances such as water, carbon dioxide and compost.
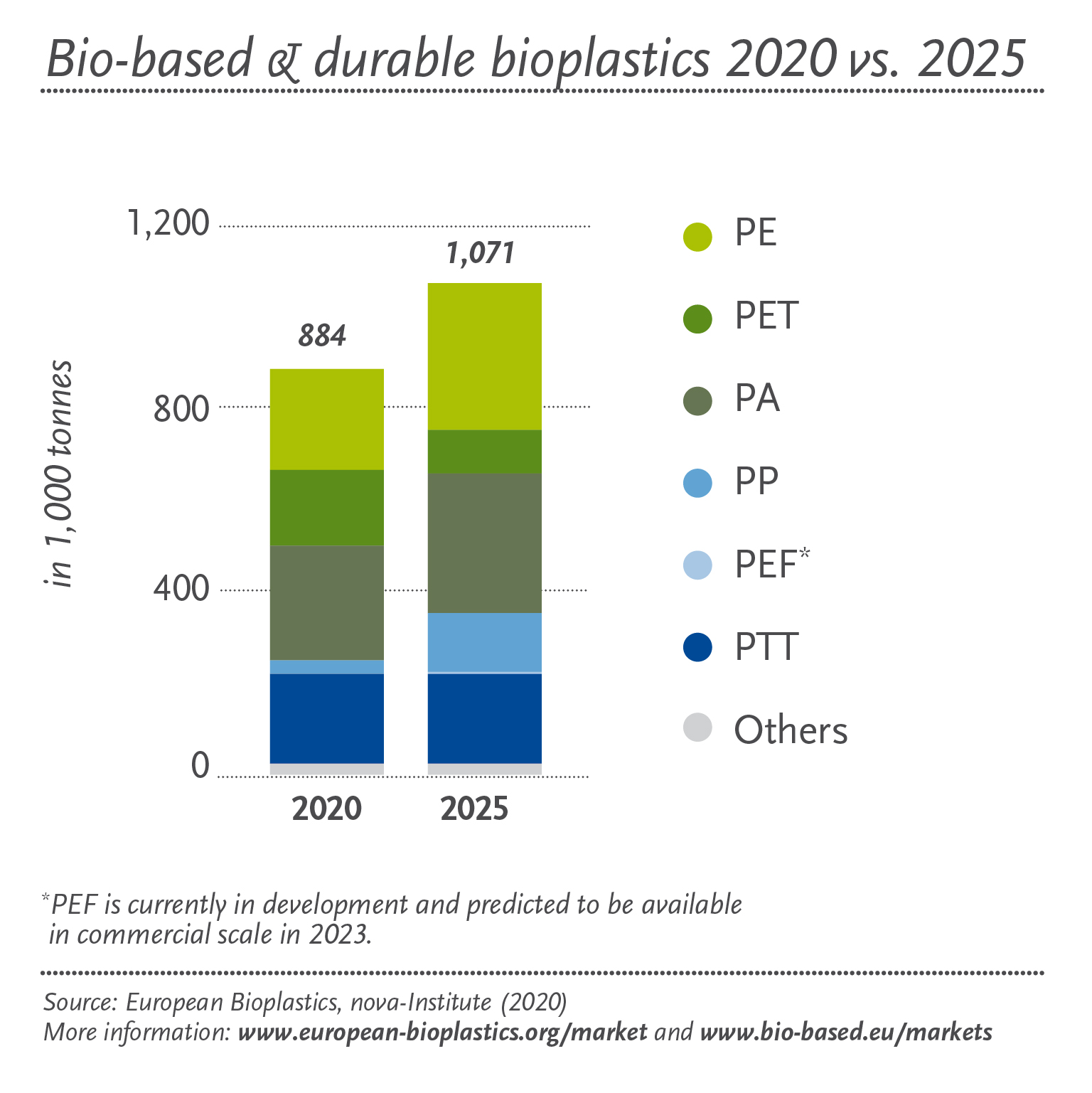
Biobased plastics: an environmentally friendly alternative
On the positive side, more and more applications are being developed for biobased and/or biodegradable plastics such as PLA, PHA or PBS.
Biobased plastics are gaining weight in the European Industry model and production and capacities continue to grow.
This type of material can be a sustainable and respectful alternative for our planet, which is a necessary step towards achieving a more responsible, modern and futuroriented plastics indutry.
These bioplastics, such as PE, PET or PVC, have properties identical to their versions derived from non-renewable energy sources, such as petroleum. In other words, they are technically equivalent to their fossil counterparts but with the advantage and added value of helping to reduce the carbon footprint of a product.
HOW CAN I DIFFERENTIATE BIOBASED PLASTICS?
Companies working with bioplastics can indicate the biobased carbon content or biobased mass content of our products. As these units of measurement differ, the typical numerical percentage value will also differ and should be taken into account – especially when comparing one product with another.

Certification schemes and labels for biobased plastics are also available in the European and American standard such as the TUV Austria certificate.
Prime Biopolymers, a company specialised in development of bioplastics.







