Know the definition and types of bioplastics
Bioplastics are not just a type of material. This term encompasses a whole family of materials that may have different applications and properties.
According to European Bioplastics, a plastic material is defined as a bioplastic if it is defined biobased, biodegradable or both properties at the same time.
The term “biobased” means that a material or product is of plant origin, such as sugar cane or corn.
On the other hand, biodegradation is a chemical process by which microorganisms found in the environment are able to convert the material into natural substances such as water, carbon dioxide and compost.
Bioplastics: a sustainable alternative
Today there is an alternative for almost every type of conventional plastic and its corresponding application. Bioplastics have virtually the same performance properties as petroleum-based plastics. They also offer additional benefits such as carbon footprint reduction or composting.
Bioplastics are essentially a very important part of the bioeconomy and are rapidly developing a greater market presence, generating economic growth while reducing environmental impact.
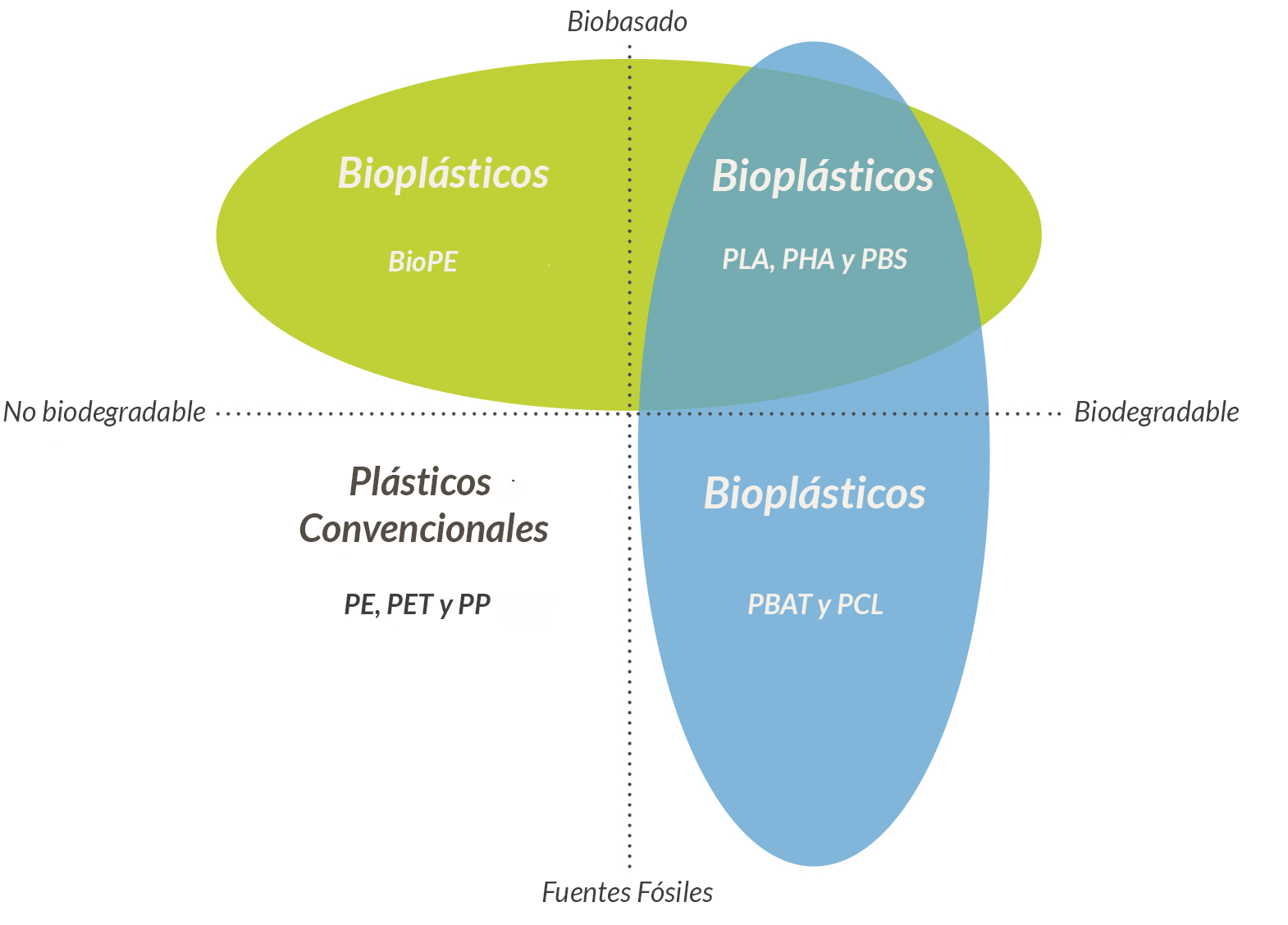
MAIN MATERIAL GROUPS OF BIOPLASTIC
There are mainly three groups of materials in bioplastics:
- Biobased plastics that are not biodegradable, such as BioPE.
- Plastics derived from fossil sources that are biodegradable, such as PBAT.
- Plastics that are biobased and biodegradable such as PLA.
The future of bioplastics
Currently, bioplastics represent a small part of the approximately 359 million tons of plastic produced each year worldwide.
However, demand is increasing and more sophisticated materials, applications and products are appearing every day, so the market is growing continuously and dynamically.
Prime Biopolymers, a company specialised in the development of bioplastics.







